

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (10): 1143-1155.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2020.01143
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Next Articles
GAO Xiaolei1, LI Xiaowei1, SUN Min1, BAI Xuejun2( ), GAO Lei1,3(
), GAO Lei1,3( )
)
Received:2020-01-08
Published:2020-10-25
Online:2020-08-24
Contact:
BAI Xuejun,GAO Lei
E-mail:bxuejun@126.com;gaolei1983good@sina.cn
Supported by:GAO Xiaolei, LI Xiaowei, SUN Min, BAI Xuejun, GAO Lei. (2020). The word frequency effect of fovea and its effect on the preview effect of parafovea in Tibetan reading. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 52(10), 1143-1155.
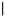 ” means the boundary position, and the subject is not visible during the experiment. “
” means the boundary position, and the subject is not visible during the experiment. “ 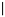
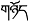
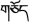

Figure 1. Boundary paradigm diagram. Note. “” means the boundary position, and the subject is not visible during the experiment. “ ” is the preview word, “ ” is the target word. There are countless Fridays in a year.
| Languages | Language type | Structure | Word/Word mark | Transparency | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alphabetic writing | Ideographic writing | Linear structure | Three-dimensional structure | Separator character | Blank space | Pronounced transparency | pronounced opaque | |
| Tibetan | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| English | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Chinese | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
Table 1 A comparative study of Tibetan, English and Chinese
| Languages | Language type | Structure | Word/Word mark | Transparency | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alphabetic writing | Ideographic writing | Linear structure | Three-dimensional structure | Separator character | Blank space | Pronounced transparency | pronounced opaque | |
| Tibetan | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| English | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Chinese | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
| Group | Frequency of words (counts/million) | Word length (number of characters) |
|---|---|---|
| High frequency group | 301 ± 625 | 4.05 ± 1.01 |
| Low frequency group | 26 ± 153 | 4.50 ± 1.13 |
Table 2 Mean and standard deviation of word frequency and word length for noun n (M ± SD)
| Group | Frequency of words (counts/million) | Word length (number of characters) |
|---|---|---|
| High frequency group | 301 ± 625 | 4.05 ± 1.01 |
| Low frequency group | 26 ± 153 | 4.50 ± 1.13 |
| Word frequency | First fixation duration (ms) | Gaze duration (ms) | Total fixation duration (ms) | Total fixation counts (counts) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High frequency | 256 ± 47 | 430 ± 180 | 749 ± 338 | 2.9 ± 1.1 |
| Low frequency | 265 ± 42 | 511 ± 219 | 909 ± 404 | 3.5 ± 1.4 |
Table 3 The mean value and standard deviation (M ± SD) of each eye movement indexes of noun n under different conditions
| Word frequency | First fixation duration (ms) | Gaze duration (ms) | Total fixation duration (ms) | Total fixation counts (counts) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High frequency | 256 ± 47 | 430 ± 180 | 749 ± 338 | 2.9 ± 1.1 |
| Low frequency | 265 ± 42 | 511 ± 219 | 909 ± 404 | 3.5 ± 1.4 |
| Word frequency | First fixation duration (ms) | Gaze duration (ms) | Total fixation duration (ms) | Total fixation counts (counts) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High frequency | 257 ± 41 | 415 ± 134 | 677 ± 266 | 2.6 ± 0.9 |
| Low frequency | 269 ± 48 | 432 ± 148 | 706 ± 272 | 2.7 ± 1.0 |
Table 4 The mean value and standard deviation (M ± SD) of each eye movement indexes of adjectives n+1 under different conditions
| Word frequency | First fixation duration (ms) | Gaze duration (ms) | Total fixation duration (ms) | Total fixation counts (counts) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High frequency | 257 ± 41 | 415 ± 134 | 677 ± 266 | 2.6 ± 0.9 |
| Low frequency | 269 ± 48 | 432 ± 148 | 706 ± 272 | 2.7 ± 1.0 |
| Group | Frequency of words (counts/million) | Word length (number of characters) |
|---|---|---|
| High frequency group | 244 ± 493 | 3.88 ± 1.15 |
| Low frequency group | 16 ± 13 | 4.55 ± 1.08 |
Table 5 Mean and standard deviation of word frequency and word length for noun (M ± SD)
| Group | Frequency of words (counts/million) | Word length (number of characters) |
|---|---|---|
| High frequency group | 244 ± 493 | 3.88 ± 1.15 |
| Low frequency group | 16 ± 13 | 4.55 ± 1.08 |
| Preview word | Frequency of words (counts/million) | Word length (number of characters) |
|---|---|---|
| Same preview | 375 ± 247 | 2.85 ± 0.09 |
| Homophonic preview | 256 ± 297 | 2.55 ± 0.12 |
| Font-like preview | 354 ± 323 | 2.72 ± 0.88 |
Table 6 Mean and standard deviation (M ± SD) of word frequency and word length of the three previews
| Preview word | Frequency of words (counts/million) | Word length (number of characters) |
|---|---|---|
| Same preview | 375 ± 247 | 2.85 ± 0.09 |
| Homophonic preview | 256 ± 297 | 2.55 ± 0.12 |
| Font-like preview | 354 ± 323 | 2.72 ± 0.88 |
| Conditions | First fixation duration (ms) | Gaze duration (ms) | Total fixation duration (ms) | Total fixation counts (counts) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Same high frequency | 276 ± 76 | 376 ± 162 | 642 ± 311 | 2.2 ± 0.8 |
| High Frequency homophony | 262 ± 66 | 333 ± 94 | 525 ± 205 | 2.0 ± 0.6 |
| High frequency similarity | 238 ± 62 | 296 ± 102 | 546 ± 306 | 2.1 ± 0.8 2.1 ± 0.8 |
| High frequency control | 299 ± 63 | 387 ± 98 | 675 ± 245 | 2.6 ± 0.8 |
| Same low frequency | 261 ± 75 | 342 ± 133 | 597 ± 285 | 2.1 ± 0.9 |
| Low tone | 244 ± 59 | 327 ± 100 | 505 ± 211 | 2.0 ± 0.7 |
| Low frequency similarity | 266 ± 91 | 325 ± 88 | 517 ± 187 | 2.0 ± 0.7 |
| Low frequency control | 296 ± 74 | 383 ± 113 | 714 ± 282 | 2.0 ± 1.0 |
Table 7 The mean value and standard deviation (M ± SD) of each eye movement indexes on the target words
| Conditions | First fixation duration (ms) | Gaze duration (ms) | Total fixation duration (ms) | Total fixation counts (counts) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Same high frequency | 276 ± 76 | 376 ± 162 | 642 ± 311 | 2.2 ± 0.8 |
| High Frequency homophony | 262 ± 66 | 333 ± 94 | 525 ± 205 | 2.0 ± 0.6 |
| High frequency similarity | 238 ± 62 | 296 ± 102 | 546 ± 306 | 2.1 ± 0.8 2.1 ± 0.8 |
| High frequency control | 299 ± 63 | 387 ± 98 | 675 ± 245 | 2.6 ± 0.8 |
| Same low frequency | 261 ± 75 | 342 ± 133 | 597 ± 285 | 2.1 ± 0.9 |
| Low tone | 244 ± 59 | 327 ± 100 | 505 ± 211 | 2.0 ± 0.7 |
| Low frequency similarity | 266 ± 91 | 325 ± 88 | 517 ± 187 | 2.0 ± 0.7 |
| Low frequency control | 296 ± 74 | 383 ± 113 | 714 ± 282 | 2.0 ± 1.0 |
| 1 |
Angele, B., Slattery, T. J., Yang, J. M., Kliegl, R., & Rayner, K . ( 2008). Parafoveal processing in reading: Manipulating n+1 and n+2 previews simultaneously. Visual Cognition, 16( 6), 697-707.
doi: 10.1080/13506280802009704 URL pmid: 19424452 |
| 2 |
Ashby, J., Treiman, R., Kessler, B., & Rayner, K . ( 2006). Vowel processing during silent reading: Evidence from eye movements. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 32( 2), 416-424.
doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.32.2.416 URL pmid: 16569156 |
| 3 |
Bai, X. J., Gao, X. L., Gao, L., & Wang, Y. S . ( 2017). An eye movement study on the perceptual span in reading Tibetan language. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 49( 5), 569-576.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2017.00569 URL |
| 4 | Bai, X. J., Li, X., Yan, G. L . ( 2015). Eye movement control in Chinese reading: A summary over the past 20 years of research. Psychological Development and Education, 31( 1), 85-91. |
| 5 | Bai, X. J., Liu, J., Zang, C. L., Zhang, M. M., Guo, X. F., & Yan, G. L . ( 2011). The advance of parafoveal preview effects in Chinese reading. Advances in Psychological Science, 19( 12), 1721-1729. |
| 6 | Bai, X. J., Zang, C. L., Yan, G. L., & Shen, D. L ., ( 2006, May). The role of different linguistic codes in parafoveal processing. The 2nd China Internal Conference on Eye Movements, China, Tianjin. |
| 7 |
Chace, K. H., Rayner, K., & Well, A. D . ( 2005). Eye movements and phonological parafoveal preview: Effects of reading skill. Canadian Journal of Experimental Psychology, 59( 3), 209-217.
doi: 10.1037/h0087476 URL pmid: 16248500 |
| 8 | Ding, H. L . ( 2017). Study on the distribution and statistical of the structure Tibetan Noun Phrases (Unpublished master’s thesis). Northwest Minzu University. |
| 9 |
Drieghe, D., Rayner, K., & Pollatsek, A . ( 2005). Eye movements and word skipping during reading revisited. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 31( 5), 954-969.
doi: 10.1037/0096-1523.31.5.954 URL pmid: 16262491 |
| 10 |
Drieghe, D., Rayner, K., & Pollatsek, A . ( 2008). Mislocated fixations can account for parafoveal-on-foveal effects in eye movements during reading. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 61( 8), 1239-1249.
doi: 10.1080/17470210701467953 URL pmid: 17853202 |
| 11 |
Gao, M., Li, L., Xiang, H. W., Sui, X., & Radach, R . ( 2017). Parafoveal preview benefits during silent and oral reading. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 49( 11), 1357-1369.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2017.01357 URL |
| 12 | Gao, X. L., Wang, Y. S., Guo, Z. Y., Zhang, M. M., & Bai, X. J . ( 2015). The characteristics of semantic and lexical representation of Tibetan-Chinese bilinguals. Studies of Psychology and Behavior, 13( 6), 737-743. |
| 13 | Henderson J. M., & Ferreira, F. ( 1990). Effects of foveal processing difficulty on the perceptual span in reading: Implications for attention and eye movement control. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 16( 3), 417-429. |
| 14 |
Henderson, J. M., & Ferreira, F. ( 1993). Eye movement control during reading: Fixation measures reflect foveal but not parafoveal processing difficulty. Canadian Journal of Experimental Psychology, 47( 2), 201-221.
URL pmid: 8364530 |
| 15 |
Hohenstein, S., Laubrock, J., & Kliegl, R . ( 2010). Semantic preview benefit in eye movements during reading: A parafoveal fast-priming study. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 36( 5), 1150-1170.
doi: 10.1037/a0020233 URL pmid: 20804291 |
| 16 |
Joseph, H. S. S. L., Nation, K., & Liversedge, S. P . ( 2013). Using eye movements to investigate word frequency effects in children’s sentence reading. School Psychology Review, 42( 2), 207-222.
doi: 10.1080/02796015.2013.12087485 URL |
| 17 |
Kennedy, A., Pynte, J., & Ducrot, S . ( 2002). Parafoveal-on-foveal interactions in word recognition. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 55( 4), 1307-1337.
doi: 10.1080/02724980244000071 URL pmid: 12420997 |
| 18 |
Kliegl, R., Grabner, E., Rolfs, M., & Engbert, R . ( 2004). Length, frequency, and predictability effects of words on eye movements in reading. European Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 16( 1-2), 262-284.
doi: 10.1080/09541440340000213 URL |
| 19 |
Kliegl, R., Nuthmann, A., & Engbert, R . ( 2006). Tracking the mind during reading: The influence of past, present, and future words on fixation durations. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 135( 1), 12-35.
doi: 10.1037/0096-3445.135.1.12 URL |
| 20 |
Lavigne, F., Vitu, F., & d’Ydewalle, G . ( 2000). The influence of semantic context on initial eye landing sites in words. Acta Psychologica, 104( 2), 191-214.
doi: 10.1016/s0001-6918(00)00020-2 URL pmid: 10900705 |
| 21 |
Li, N., Wang, S. P., Mo, L. X., & Kliegl, R . ( 2017). Contextual constraint and preview time modulate the semantic preview effect: Evidence from Chinese sentence reading. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 71( 1), 241-249.
doi: 10.1080/17470218.2017.1310914 URL |
| 22 | Li, X., Li, H. C., Liu, J. Y., & Bai, X. J . ( 2017). Effects of reading level and reading task on English word frequency: Evidence from eye movements for Chinese-English bilinguals during English reading. Studies of Psychology and Behavior, 15( 4), 455-461. |
| 23 | Li, X. S., Liu, P. P., & Ma, G. J . ( 2011). Advances in cognitive mechanisms of word segmentation during Chinese reading. Advances in Psychological Science, 19( 4), 459-470. |
| 24 |
Liu, W. M., Inhoff, A. W., Ye, Y., & Wu, C. L . ( 2002). Use of parafoveally visible characters during the reading of Chinese sentences. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 28( 5), 1213-1227.
doi: 10.1037//0096-1523.28.5.1213 URL pmid: 12421066 |
| 25 |
Liu, Y. P., Huang, R., Gao, D. G., & Reichle, E. D . ( 2017). Further tests of a dynamic-adjustment account of saccade targeting during the reading of Chinese. Cognitive Science, 41( 6), 1264-1287.
doi: 10.1111/cogs.2017.41.issue-S6 URL |
| 26 |
Liu, Y. P., Reichle, E. D., & Li, X. S . ( 2015). Parafoveal processing affects outgoing saccade length during the reading of Chinese. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 41( 4), 1229-1236.
doi: 10.1037/xlm0000057 URL pmid: 25181495 |
| 27 | Lu, Y. J. (2007). Modern Tibetan frequency dictionary. Beijing: The Ethnic Publishing House. |
| 28 |
Ma, G. J., &Li, X. S . ( 2012). Attention allocation during reading: Sequential or parallel. Advances in Psychological Science, 20( 11), 1755-1767.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2012.01755 URL |
| 29 |
Miellet, S., & Sparrow, L. ( 2004). Phonological codes are assembled before word fixation: Evidence from boundary paradigm in sentence reading. Brain and Language, 90( 1-3), 299-310.
doi: 10.1016/S0093-934X(03)00442-5 URL pmid: 15172547 |
| 30 |
Niefind, F., & Dimigen, O. ( 2016). Dissociating parafoveal preview benefit and parafovea-on-fovea effects during reading: A combined eye tracking and EEG study. Psychophysiology, 53( 12), 1784-1798.
doi: 10.1111/psyp.12765 URL pmid: 27680711 |
| 31 |
Payne, B. R., Stites, M. C., & Federmeier, K. D . ( 2016). Out of the corner of my eye: Foveal semantic load modulates parafoveal processing in reading. Journal of Experimental Psychology Human Perception & Performance, 42( 11), 1839-1857.
doi: 10.1037/xhp0000253 URL pmid: 27428778 |
| 32 |
Perea, M., Tejero, P., & Winskel, H . ( 2015). Can colours be used to segment words when reading? Acta Psychologica, 159, 8-13.
doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2015.05.005 URL pmid: 26002618 |
| 33 |
Pollatsek, A., Juhasz, B. J., Reichle, E. D., Machacek, D., & Rayner, K . ( 2008). Immediate and delayed effects of word frequency and word length on eye movements in reading: A reversed delayed effect of word length. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 34( 3), 726-750.
doi: 10.1037/0096-1523.34.3.726 URL pmid: 18505334 |
| 34 |
Pollatsek, A., Lesch, M., Morris, R. K., & Rayner, K . ( 1992). Phonological codes are used in integrating information across saccades in word identification and reading. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 18( 1), 148-162.
doi: 10.1037//0096-1523.18.1.148 URL pmid: 1532185 |
| 35 |
Pollatsek, A., & Rayner, K. ( 1982). Eye movement control in reading: The role of word boundaries. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 8( 6), 817-833.
doi: 10.1037/0096-1523.8.6.817 URL |
| 36 |
Pollatsek, A., Tan, L. H., & Rayner, K . ( 2000). The role of phonological codes in integrating information across saccadic eye movements in Chinese character identification. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 26( 2), 607-633.
doi: 10.1037//0096-1523.26.2.607 URL pmid: 10811166 |
| 37 |
Radach, R., & Kennedy, A. ( 2013). Eye movements in reading: Some theoretical context. The Quarterly journal of experimental psychology, 66( 3), 429-452.
doi: 10.1080/17470218.2012.750676 URL pmid: 23289943 |
| 38 |
Rayner, K. ( 1975). The perceptual span and peripheral cues in reading. Cognitive Psychology, 7( 1), 65-81.
doi: 10.1016/0010-0285(75)90005-5 URL |
| 39 |
Rayner, K. ( 1986). Eye movements and the perceptual span in beginning and skilled readers. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 41( 2), 211-236.
doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(86)90037-8 URL pmid: 3701249 |
| 40 |
Rayner, K. ( 1998). Eye movements in reading and information processing: 20 years of research. Psychological Bulletin, 124( 3), 372-422.
doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.124.3.372 URL pmid: 9849112 |
| 41 |
Rayner, K. ( 2009). Eye movements and attention in reading, scene perception, and visual search. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 62( 8), 1457-1506.
doi: 10.1080/17470210902816461 URL pmid: 19449261 |
| 42 |
Sheena, K. A. Y., Johanna, K. K., Simon, P. L., & Valerie, B . ( 2015). Processing of written irony in autism spectrum disorder: An eye-movement study. Autism Research, 8( 6), 749-760.
URL pmid: 25962666 |
| 43 |
Sommer, W., Li, N., Niefind, F., Dimigen, O., & Wang, S. P . ( 2014). Parafoveal preview effects in alphabetic language and Chinese: Evidence from ERP/eye movement coregistration. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 94( 2), 178-179.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2014.08.757 URL |
| 44 | Tong, W., Liu, N. N., Fu, G. & Yan, G. L. . ( 2014). The perceptual span in Chinese when reading sentence constructed by one-character words. Studies of Psychology and Behavior, 12( 3), 298-303. |
| 45 |
Tsai, J. L., Kliegl, R., & Yan, M . ( 2012). Parafoveal semantic information extraction in traditional Chinese reading. Acta Psychologica, 141( 1), 17-23.
URL pmid: 22820455 |
| 46 |
Tsai, J. L., Lee, C. Y., Tzeng, O. J. L., Hung, D. L., & Yen, N. S . ( 2004). Use of phonological codes for Chinese characters: Evidence from processing of parafoveal preview when reading sentences. Brain and Language, 91( 2), 235-244.
doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2004.02.005 URL |
| 47 |
Unsworth, S. J., &, Pexman, P., M . ( 2003). The impact of reader skill on phonological processing in visual word recognition. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology Section A: Human Experimental Psychology, 56( 1), 63-81.
doi: 10.1080/02724980244000206 URL |
| 48 | Veldre, A., & Andrews, S. ( 2016). Semantic preview benefit in English: Individual differences in the extraction and use of parafoveal semantic information. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning Memory & Cognition, 42( 6), 837-854. |
| 49 |
Vorstius, C., Radach, R., & Lonigan, C. J . ( 2014). Eye movements in developing readers: A comparison of silent and oral sentence reading. Visual Cognition, 22( 3-4), 458-485.
doi: 10.1080/13506285.2014.881445 URL |
| 50 | Wan, M. Z. X., &Ni, M. Z. X. ( 2018). Study on the structure rules of nominal phrases in modern Tibetan. Plateau Science Reasearch, 2( 1), 89-93. |
| 51 |
Wang, C. A., &, Inhoff, A., W . ( 2010). The influence of visual contrast and case changes on parafoveal preview benefits during reading. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 63( 4), 805-817.
doi: 10.1080/17470210903147494 URL pmid: 19742385 |
| 52 | Wang, S. P., Tong, X. H., Yang, J. M., & Leng, Y . ( 2009). Semantic codes are obtained before word fixation in Chinese sentence reading: Evidence from eye-movements. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 41( 3), 220-232. |
| 53 | Wang, Y. S . ( 2016). The parafoveal processing influence selection of target during Chinese reading (Unpublished doctorial dissertation). Tianjin Normal University, China. |
| 54 |
Wang, Y. S., Zhao, B. J., Chen, M. J., Li, X., Yan, G. L., & Bai, X. J . ( 2018). Influence of the frequency of fixated words and the number of strokes of parafoveal words on saccadic target selection in Chinese reading. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 50( 12), 1336-1345.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2018.01336 URL |
| 55 |
White, S. J., Rayner, K., & Liversedge, S. P . ( 2005a). The influence of parafoveal word length and contextual constraint on fixation durations and word skipping in reading. Psychonomic Bulletin and Review, 12( 3), 466-471.
doi: 10.3758/bf03193789 URL pmid: 16235630 |
| 56 |
White, S. J., Rayner, K., & Liversedge, S. P . ( 2005b). Eye movements and the modulation of parafoveal processing by foveal processing difficulty: A reexamination. Psychonomic Bulletin and Review, 12( 5), 891-896.
doi: 10.3758/bf03196782 URL pmid: 16524007 |
| 57 | Yan, G. L., Bai, X. J., & Chen, X. Y . ( 2003). Review of eye movement theories on reading. Studies of Psychology and Behavior, 1( 2), 156-160. |
| 58 | Yan, G. L., Tao, J. Y., Meng, Z., & Jiang, K . ( 2019). Parafoveal processing of character n+1 of deaf readers. Journal of Psychological Science, 42( 4), 997-1003. |
| 59 | Yan, G. L., Wang, L. H., Wu, J. G., & Bai, X. J . ( 2011). The perceptual span and parafoveal preview effect of fifth graders and college students: An eye movement study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 43( 3), 249-263. |
| 60 | Yan, G. L., Wu, J. G., Hu, Y. W., & Bai, X. J . ( 2010). Review of eye movement research paradigms in reading. Advances in Psychological Science, 18( 12), 1966-1976. |
| 61 |
Yan, G. L., Xiong, J. P., Zang, C. L., Yu, L. L., Cui, L., & Bai, X. J . ( 2013). Review of eye-movement measures in reading research. Advances in Psychological Science, 21( 4), 589-605.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2013.00589 URL |
| 62 | Yan, M . ( 2015). Visually complex foveal words increase the amount of parafoveal information acquired. Vision Research, 111( PtA), 91-96. |
| 63 |
Yan, M., Richter, E. M., Shu, H., & Kliegl, R . ( 2009). Readers of Chinese extract semantic information from parafoveal words. Psychonomic Bulletin and Review, 16( 3), 561-566.
doi: 10.3758/PBR.16.3.561 URL pmid: 19451385 |
| 64 |
Yang, J. M., Wang, S. P., Tong, X. H., & Rayner, K . ( 2012). Semantic and plausiblisity effects on preview benefit during eye fixations in Chinese reading. Reading and Writing, 25( 5), 1031-1052.
URL pmid: 22593624 |
| 65 |
Yang, J. M., Wang, S. P., Xu, Y. M., & Rayner, K . ( 2009). Do Chinese readers obtain preview benefit from word n+2? Evidence from eye movements. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 35( 4), 1192-1204.
doi: 10.1037/a0013554 URL pmid: 19653758 |
| 66 |
Yen, M. H., Tsai, J. L., Tzeng, O. J. L., & Hung, D. L . ( 2008). Eye movements and parafoveal word processing in reading Chinese. Memory and Cognition, 36( 5), 1033-1045.
doi: 10.3758/mc.36.5.1033 URL pmid: 18630209 |
| 67 | Yin, W. B . ( 2014). Characteristics and significance of Tibetan grammar study in China in the early 21st century. China Tibetology,( 3), 198-205. |
| 68 | Zang, C. L., Meng, H. X., Bai, X. J., & Yan, G. L . ( 2013). Advances in landing position effect during reading. Journal of Psychological Science, 36( 4), 770-775. |
| 69 |
Zhang, J. J., &Cui, Z. L. ( 2008). Language switching and switching cost in Tibetan-Mandarin-English’ visual word recognition. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 40( 2), 136-147.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2008.00136 URL |
| 70 | Zhang, M. M . ( 2015). The mechanism of word skipping in Chinese reading: An eye movement study (Unpublished doctorial dissertation). Tianjin Normal University, China. |
| 71 | Zhang, W. J., Li, N., Guan, S. W., & Wang, S. P . ( 2014). Extraction of semantic information from parafoveal words in the reading of Chinese: An ERPs study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 46( 9), 1261-1270. |
| 72 |
Zhang, W. J., Li, N., Wang, X. Y., & Wang, S. P . ( 2015). Integration of sentence-level semantic information in parafovea: Evidence from the rsvp-flanker paradigm. Plos One, 10( 9), e0139016.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139016 URL pmid: 26418230 |
| 73 |
Zhang, W. J., Zhen, A. N., Liang, B., & Mo, L. X . ( 2019). The parallel mechanism of semantic context influences and parafoveal word identification. Neuroscience letters, 704, 73-77.
doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.03.026 URL pmid: 30936035 |
| 74 | Zhang, X. F., &Ye, W. L . ( 2006). Review of oculomotor measures in current reading research. Studies of Psychology and Behavior, 4( 3), 236-240. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||