

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (9): 1540-1552.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2025.1540
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
QIN Kuiyuan1,2, LIU Yu3,4, LIU Saifang3,4, WANG Shuo3,4, LIU Peng1,2, YOU Xuqun3,4( ), LI Yuan3,4(
), LI Yuan3,4( )
)
Published:2025-09-25
Online:2025-06-26
Contact:
YOU Xuqun,LI Yuan
E-mail:youxuqun@snnu.edu.cn;liyuan001@snnu.edu.cn
QIN Kuiyuan, LIU Yu, LIU Saifang, WANG Shuo, LIU Peng, YOU Xuqun, LI Yuan. (2025). The impact of time structure cues on prediction motion tasks in the interruption paradigm. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 57(9), 1540-1552.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2025.1540
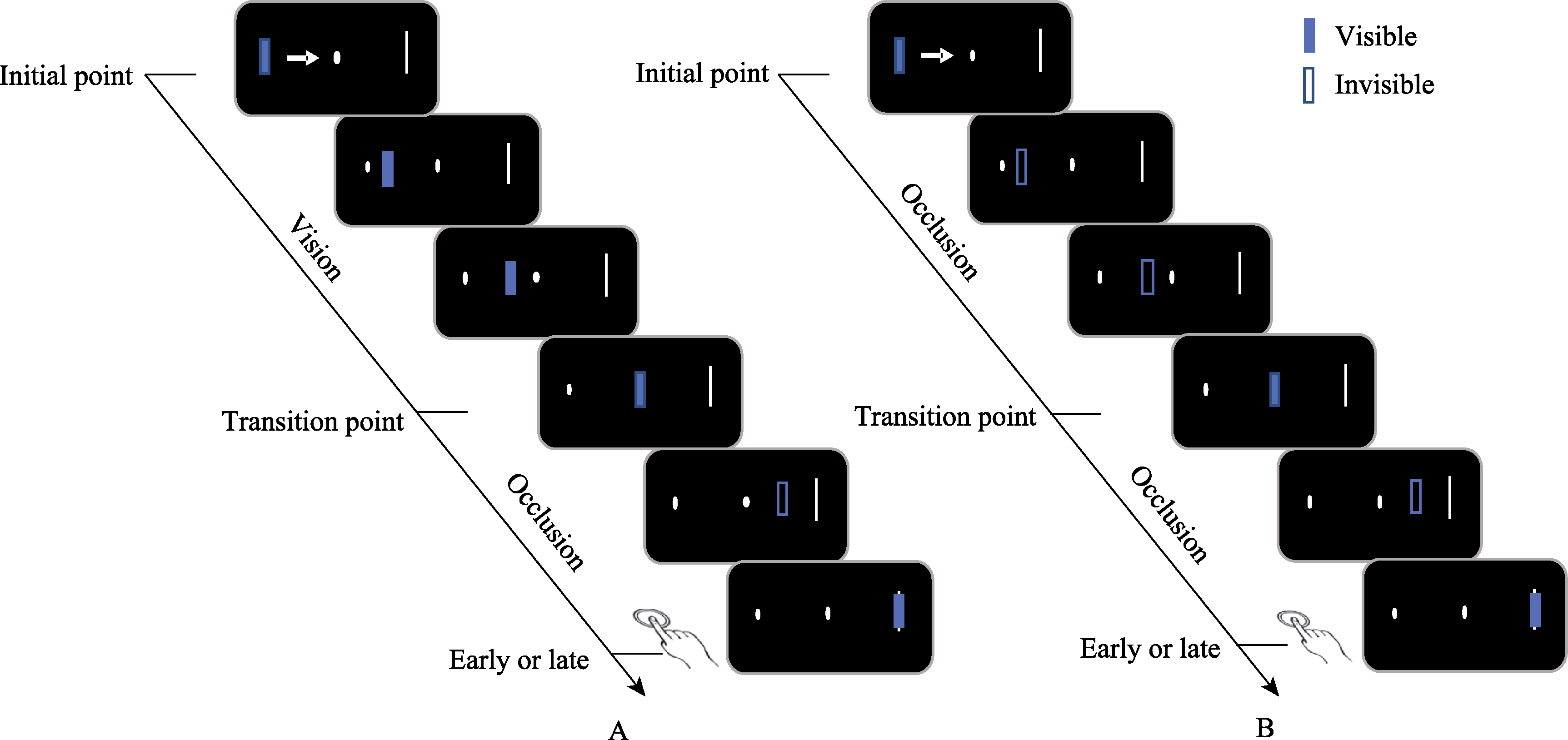
Figure 1. Schematic diagrams of Experiment 1 and Experiment 2. In Experiment 1, the movement stimulus travels from the starting point to the target position. When it reaches the occlusion point, it is occluded. After a period of time, the movement stimulus reappears at the target position, and participants are required to judge whether the stimulus arrived at this position ahead of schedule or delayed. Experiment 2 shares a similar task format with Experiment 1, but with one difference: the movement of the stimulus between the starting point and the occlusion point is also occluded. Both diagrams in the figure use an example where the temporal structure is identical (T = 1.0). For color figures, please refer to the electronic version, and the same applies hereinafter.
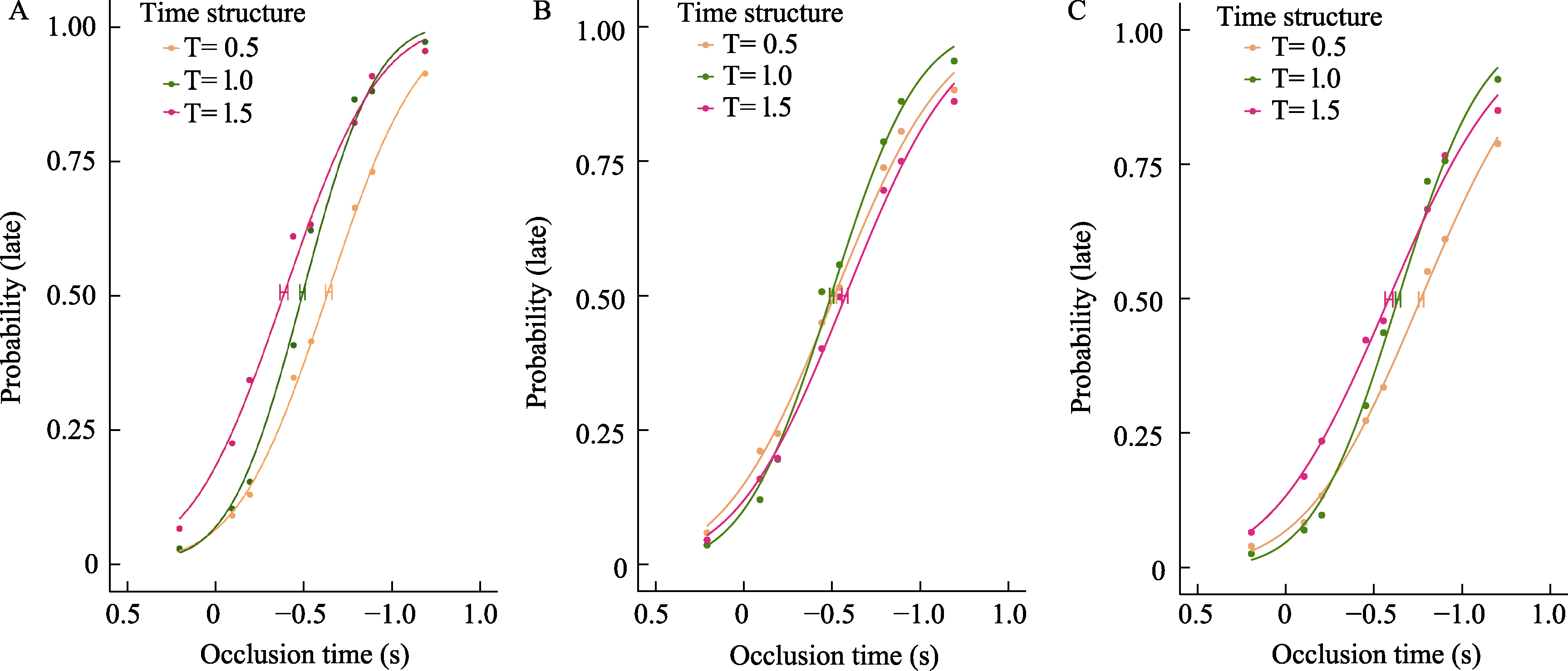
Figure 2. Logistic function fitting curves of the percentage of participants' key presses for “late”. A, B, and C represent Experiment 1, Experiment 2, and Experiment 3, respectively.
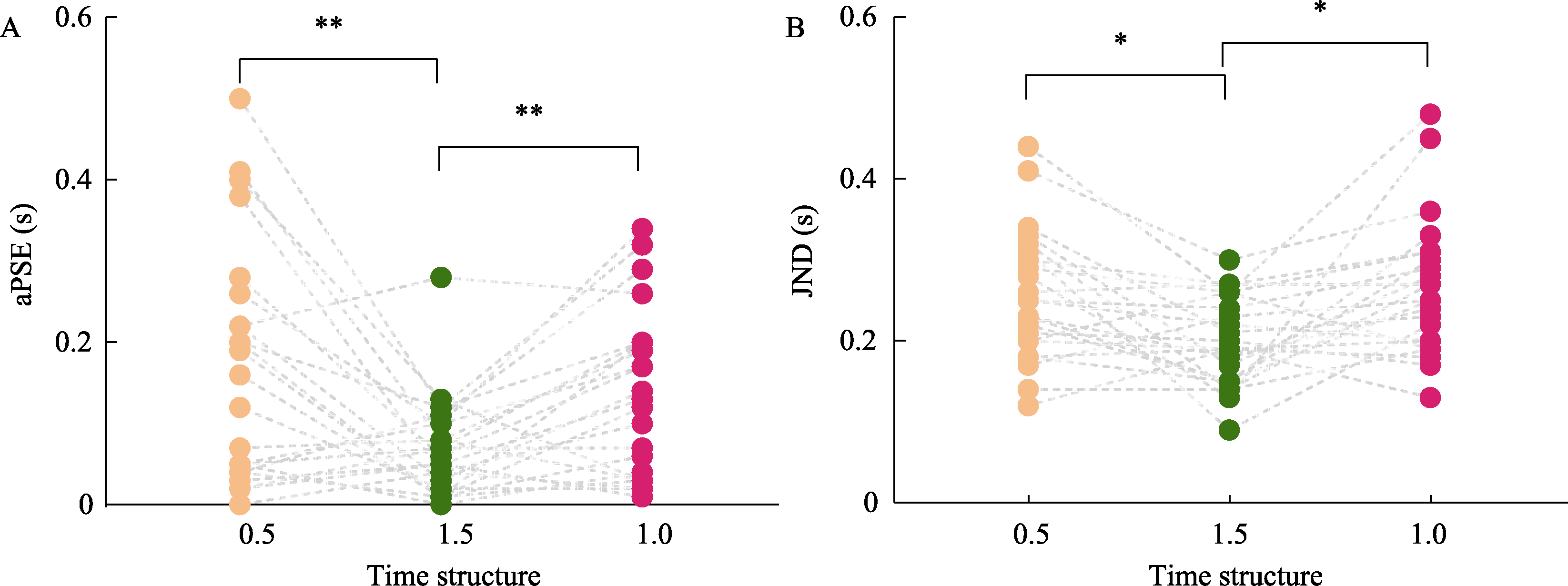
Figure 3. Panel A: Comparison chart of aPSE under three temporal structure conditions in Experiment 1. Panel B: Comparison chart of JND under three temporal structure conditions in Experiment 1. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, **p < 0.001. The same applies below.
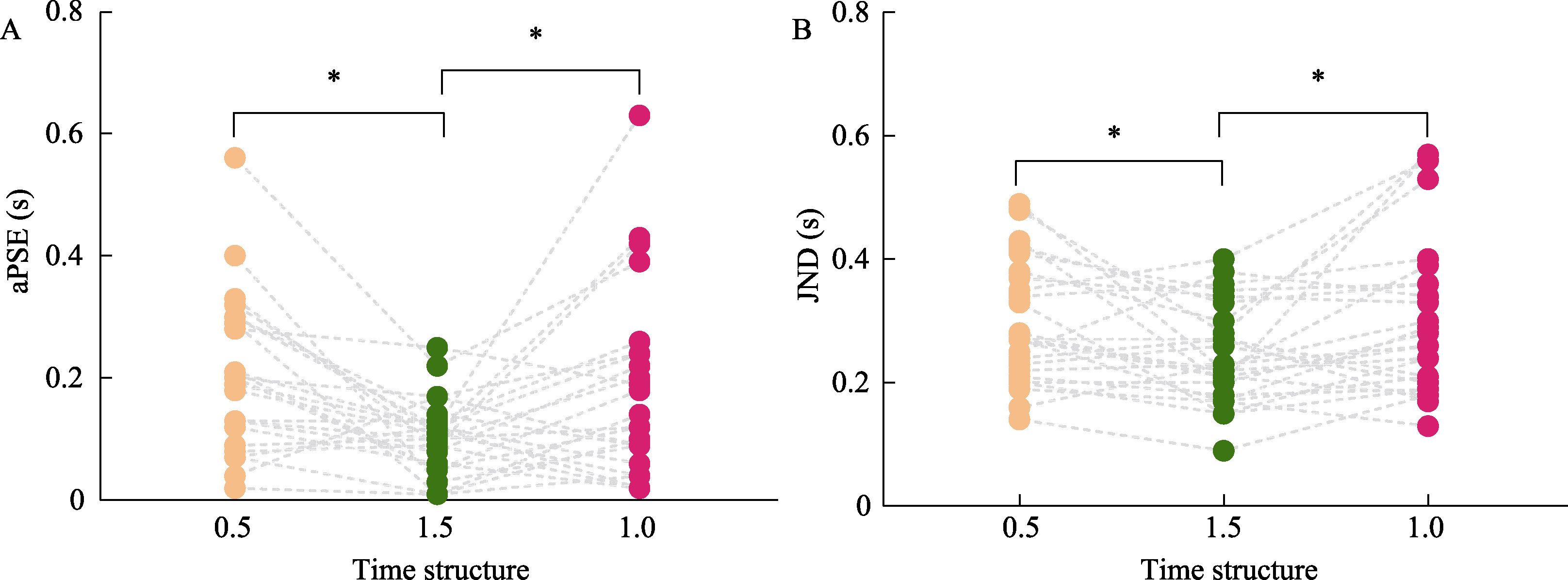
Figure 4. Panel A: Comparison chart of aPSE under three temporal structure conditions in Experiment 2. Panel B: Comparison chart of JND under three temporal structure conditions in Experiment 2.
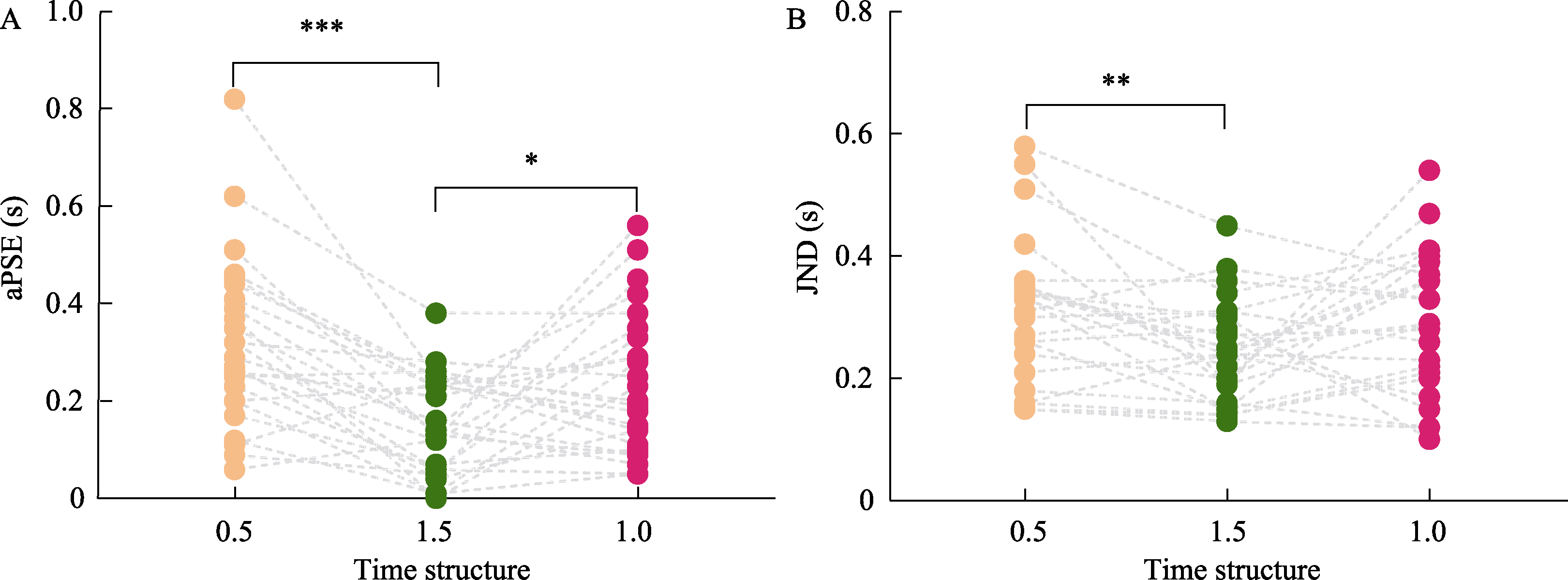
Figure 5. Panel A: Comparison chart of aPSE under three temporal structure conditions in Experiment 3. Panel B: Comparison chart of JND under three temporal structure conditions in Experiment 3.
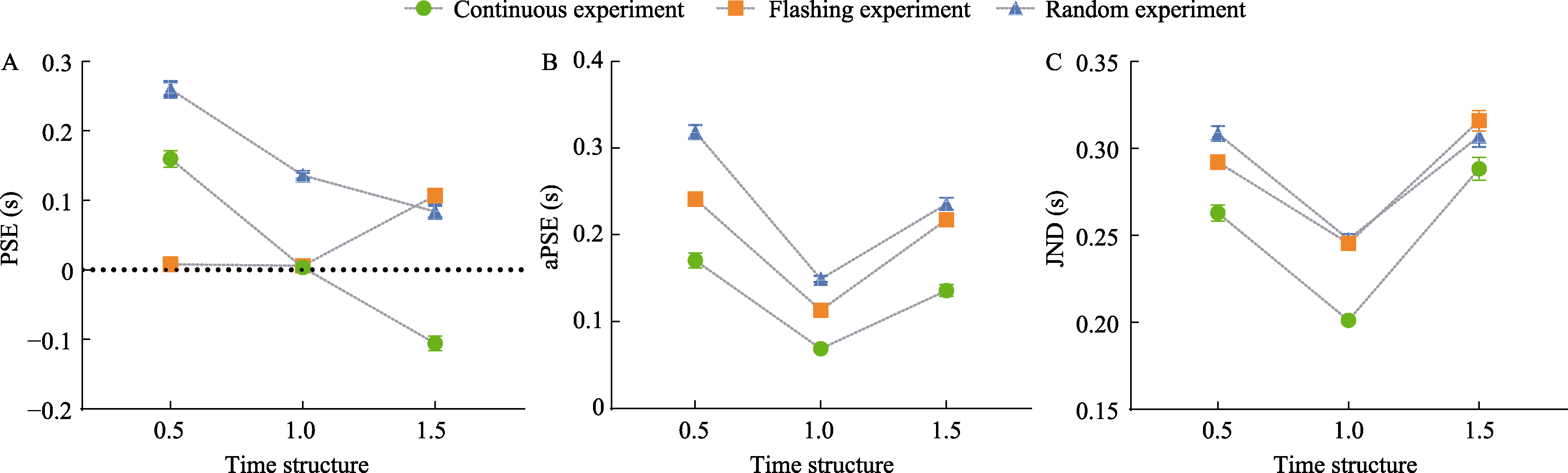
Figure 6. Panel A: Comparison of PSE across different temporal structure conditions in the three experiments. Panel B: Comparison of aPSE across different temporal structure conditions in the three experiments. Panel C: Comparison of PSE across different temporal structure conditions in the three experiments. Error bars represent standard errors.
| [1] |
Alais, D., & Blake, R. (1998). Interactions between global motion and local binocular rivalry. Vision Research, 38(5), 637-644.
pmid: 9604095 |
| [2] |
Barnes, G. R. (2008). Cognitive processes involved in smooth pursuit eye movements. Brain and Cognition, 68(3), 309-326.
doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2008.08.020 pmid: 18848744 |
| [3] |
Bauer, F., Cheadle, S. W., Parton, A., Müller, H. J., & Usher, M. (2009). Gamma flicker triggers attentional selection without awareness. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(5), 1666-1671.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810496106 pmid: 19124766 |
| [4] | Baurès, R., Balestra, M., Rosito, M., & VanRullen, R. (2018). The detrimental influence of attention on time-to-contact perception. Attention, Perception, and Psychophysics, 80(6), 1591-1598. |
| [5] |
Baurès, R., Fourteau, M., Thébault, S., Gazard, C., Pasquio, L., Meneghini, G., … Roux, F. E. (2021). Time-to-contact perception in the brain. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 99(2), 455-466.
doi: 10.1002/jnr.24740 pmid: 33070400 |
| [6] |
Baurès, R., Maquestiaux, F., DeLucia, P. R., Defer, A., & Prigent, E. (2018). Availability of attention affects time-to-contact estimation. Experimental Brain Research, 236(7), 1971-1984.
doi: 10.1007/s00221-018-5273-8 pmid: 29713757 |
| [7] |
Bengtsson, S. L., Ullén, F., Henrik Ehrsson, H., Hashimoto, T., Kito, T., Naito, E., Forssberg, H., & Sadato, N. (2009). Listening to rhythms activates motor and premotor cortices. Cortex, 45(1), 62-71.
doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2008.07.002 pmid: 19041965 |
| [8] |
Bennett, S. J., Baures, R., Hecht, H., & Benguigui, N. (2010). Eye movements influence estimation of time-to-contact in prediction motion. Experimental Brain Research, 206(4), 399-407.
doi: 10.1007/s00221-010-2416-y pmid: 20862463 |
| [9] |
Capizzi, M., Sanabria, D., & Correa, Á. (2012). Dissociating controlled from automatic processing in temporal preparation. Cognition, 123(2), 293-302.
doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2012.02.005 pmid: 22397820 |
| [10] | Chang, C. J., & Jazayeri, M. (2018). Integration of speed and time for estimating time to contact. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(12), E2879-E2887. |
| [11] | Chen, J. L., Penhune, V. B., & Zatorre, R. J. (2008). Listening to musical rhythms recruits motor regions of the brain. Cerebral Cortex, 18(12), 2844-2854. |
| [12] |
Correa, Á., Cona, G., Arbula, S., Vallesi, A., & Bisiacchi, P. (2014). Neural dissociation of automatic and controlled temporal preparation by transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neuropsychologia, 65, 131-136.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2014.10.023 pmid: 25447373 |
| [13] | Correa, Á., Lupiáñez, J., Milliken, B., & Tudela, P. (2004). Endogenous temporal orienting of attention in detection and discrimination tasks. Perception & Psychophysics, 66(2), 264-278. |
| [14] |
Cotti, J., Rohenkohl, G., Stokes, M., Nobre, A. C., & Coull, J. T. (2011). Functionally dissociating temporal and motor components of response preparation in left intraparietal sulcus. NeuroImage, 54(2), 1221-1230.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.09.038 pmid: 20868756 |
| [15] |
Coull, J. T., & Nobre, A. C. (2008). Dissociating explicit timing from temporal expectation with fMRI. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 18(2), 137-144.
doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2008.07.011 pmid: 18692573 |
| [16] |
Gepshtein, S., & Banks, M. S. (2003). Viewing geometry determines how vision and haptics combine in size perception. Current Biology, 13(6), 483-488.
pmid: 12646130 |
| [17] |
Grahn, J. A., & Brett, M. (2007). Rhythm and Beat Perception in motor areas of the brain. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 19(5), 893-906.
doi: 10.1162/jocn.2007.19.5.893 pmid: 17488212 |
| [18] | Guo, X., Gong, Y., Xue, Q., & Yuan, X. (2000). Time-to-collision estimation in the occlusion paradigm. Journal of Psychological Science, 23(1), 34-37. |
| [19] |
Herrmann, C. S. (2001). Human EEG responses to 1-100 Hz flicker: Resonance phenomena in visual cortex and their potential correlation to cognitive phenomena. Experimental Brain Research, 137(3-4), 346-353.
doi: 10.1007/s002210100682 pmid: 11355381 |
| [20] |
Hove, M. J., Fairhurst, M. T., Kotz, S. A., & Keller, P. E. (2013). Synchronizing with auditory and visual rhythms: An fMRI assessment of modality differences and modality appropriateness. NeuroImage, 67, 313-321.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.11.032 pmid: 23207574 |
| [21] |
Hove, M. J., Spivey, M. J., & Krumhansl, C. L. (2010). Compatibility of motion facilitates visuomotor synchronization. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 36(6), 1525-1534.
doi: 10.1037/a0019059 pmid: 20695698 |
| [22] | Hu, R., Yuan, P., Jiang, Y., & Wang, Y. (2019). The functional role of temporal structure in human perception: Behavioral evidence and neural correlates. Acta Physiologica Sinica, 71(1), 105-116. |
| [23] |
Jazayeri, M., & Shadlen, M. N. (2010). Temporal context calibrates interval timing. Nature Neuroscience, 13(8), 1020-1026.
doi: 10.1038/nn.2590 pmid: 20581842 |
| [24] |
Jones, M. R., & Boltz, M. (1989). Dynamic attending and responses to time. Psychological Review, 96(3), 459-491.
doi: 10.1037/0033-295x.96.3.459 pmid: 2756068 |
| [25] |
Jones, M. R., Johnston, H. M., & Puente, J. (2006). Effects of auditory pattern structure on anticipatory and reactive attending. Cognitive Psychology, 53(1), 59-96.
pmid: 16563367 |
| [26] |
Jones, M. R., Moynihan, H., MacKenzie, N., & Puente, J. (2002). Temporal aspects of stimulus-driven attending in dynamic arrays. Psychological Science, 13(4), 313-319.
doi: 10.1111/1467-9280.00458 pmid: 12137133 |
| [27] |
Kerzel, D. (2003). Attention maintains mental extrapolation of target position: Irrelevant distractors eliminate forward displacement after implied motion. Cognition, 88(1), 109-131.
pmid: 12711155 |
| [28] | Law, D. J., Pellegrino, J. W., Mitchell, S. R., Fischer, S. C., McDonald, T. P., & Hunt, E. B. (1993). Perceptual and cognitive factors governing performance in comparative arrival-time judgments. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 19(6), 1183-1199. |
| [29] |
Lee, D. N. (1976). A theory of visual control of braking based on information about time-to-collision. Perception, 5(4), 437-459.
pmid: 1005020 |
| [30] | Lee, D. N., Young, D. S., Reddish, P. E., Lough, S., & Clayton, T. M. H. (1983). Visual timing in hitting an accelerating ball. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology Section A, 35(2), 333-346. |
| [31] | Linares, D., & López-Moliner, J. (2016). Quickpsy: An R package to fit psychometric functions for multiple groups. R Journal, 8(1), 122-131. |
| [32] | Liu, R., & Huang, X. (1991). A study on time-perceptual cues in visual motion information. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 31(1), 15-20. |
| [33] |
Lyon, D. R., & Waag, W. L. (1995). Time course of visual extrapolation accuracy. Acta Psychologica, 89(3), 239-260.
pmid: 7572268 |
| [34] | Makin, A. D. J. (2018). The common rate control account of prediction motion. Psychonomic Bulletin and Review, 25(5), 1784-1797. |
| [35] | Makin, A. D. J., & Poliakoff, E. (2011). Do common systems control eye movements and motion extrapolation? Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 64(7), 1327-1343. |
| [36] |
Miller, J. E., Carlson, L. A., & McAuley, J. D. (2013). When what you hear influences when you see: Listening to an auditory rhythm influences the temporal allocation of visual attention. Psychological Science, 24(1), 11-18.
doi: 10.1177/0956797612446707 pmid: 23160202 |
| [37] |
O’Reilly, J. X., Mesulam, M. M., & Nobre, A. C.(2008). The cerebellum predicts the timing of perceptual events. Journal of Neuroscience, 28(9), 2252-2260.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2742-07.2008 pmid: 18305258 |
| [38] | Oberfeld, D., & Hecht, H. (2008). Effects of a moving distractor object on time-to-contact judgments. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 34(3), 605-623. |
| [39] |
Pfeuty, M., Ragot, R., & Pouthas, V. (2003). When time is up: CNV time course differentiates the roles of the hemispheres in the discrimination of short tone durations. Experimental Brain Research, 151(3), 372-379.
doi: 10.1007/s00221-003-1505-6 pmid: 12819842 |
| [40] | Qin, K., Chen, W., Cui, J., Zeng, X., Li, Y., Li, Y., & You, X. (2022). The influence of time structure on prediction motion in visual and auditory modalities. Attention, Perception, and Psychophysics, 84(6), 1994-2001. |
| [41] | Qin, K., Li, Y., Chen, W., Li, Y., & You, X. (2022). Effects of time structure and velocity cues on time to collision. Journal of Psychological Science, 45(4), 803-810. |
| [42] | Qin, K., Liu, Y., Li, Y., Li, Y., & You, X. (2023). The influence of time structure on number prediction motion. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 76(8), 1862-1871. |
| [43] | Qin, K., Liu, Y., Liu, S., Li, Y., Li, Y., & You, X. (2024). Neural mechanisms for integrating time and visual velocity cues in a prediction motion task: An fNIRS study. Psychophysiology, 61(1), e14425. |
| [44] |
Sanabria, D., & Correa, Á. (2013). Electrophysiological evidence of temporal preparation driven by rhythms in audition. Biological Psychology, 92(2), 98-105.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2012.11.012 pmid: 23182877 |
| [45] |
Spencer, R. M. C., Zelaznik, H. N., Diedrichsen, J., & Ivry, R. B. (2003). Disrupted timing of discontinuous but not continuous movements by cerebellar lesions. Science, 300(5624), 1437-1439.
pmid: 12775842 |
| [46] | Tang, R., Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., & Zhao, Y. (2010). What kinds of information are used in the onset of interception with hand? Acta Psychologica Sinica, 42(4), 507-517. |
| [47] |
Teichmann, L., Edwards, G., & Baker, C. I. (2021). Resolving visual motion through perceptual gaps. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 25(11), 978-991.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2021.07.017 pmid: 34489180 |
| [48] | Tresilian, J. R. (1995). Perceptual and cognitive processes in time-to- contact estimation: Analysis of prediction-motion and relative judgment tasks. Perception & Psychophysics, 57(2), 231-245. |
| [49] |
Triviño, M., Arnedo, M., Lupiáñez, J., Chirivella, J., & Correa, Á. (2011). Rhythms can overcome temporal orienting deficit after right frontal damage. Neuropsychologia, 49(14), 3917-3930.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2011.10.009 pmid: 22019698 |
| [50] | Watamaniuk, S. N. J., & McKee, S. P. (1995). Seeing motion behind occluders. Nature, 377(6551), 729-730. |
| [51] | Zelaznik, H. N., Spencer, R. M. C., & Ivry, R. B. (2002). Dissociation of explicit and implicit timing in repetitive tapping and drawing movements. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 28(3), 575-588. |
| [1] | ZHANG Hang, WANG Ting, FENG Xiaohui, WEI Yiping, ZHANG Jijia. Effect of bronze drum training on rhythm perception and executive function of Zhuang drummers [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(11): 1762-1779. |
| [2] | ZHANG Zhenghua, HAN Mei, ZHANG Fang, LI Weijun. Musical training improves rhythm integrative processing of classical Chinese poem [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(7): 847-860. |
| [3] | ZHAO Huaiyang, JIANG Jun, ZHOU Linshu, JIANG Cunmei. Role of the human mirror system in automatic processing of musical emotion: Evidence from EEG [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(7): 795-804. |
| [4] | YIN Huazhan;LI Dan;YUAN Xiangyong;HUANG Xiting. Contrasting Effects of Dual-task Paradigm and of Timing Interruption Paradigm in Interval Timing of the Context of Culti-modal Processing [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2013, 45(8): 860-873. |
| [5] | Wang-Yunjia,Chu-Min,He-Lin. Classification and Distribution of Sentence Stress in Mandarin [J]. , 2003, 35(06): 734-742. |
| [6] | Liu Shiyi (Shanghai Institute of Physiology, Academia Sinica, Shanghai 200031, China ). SOME CONTEMPORARY THEORETICAL QUESTIONS IN SLEEP RESEARCH [J]. , 1996, 28(03): 299-306. |
| [7] | Liu Shiyi,Chen Ming,Zhang Yi,Zhang Wenyuan,Dai Xiuju Shanghai Institute of Physiology, Academia Sinica. A STUDY ON CIRCADIAN BODY TEMPERATURE “CLOCK” IN YOUNG ADULT SUBJECTS [J]. , 1993, 25(03): 42-48. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||