

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2020, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (7): 811-822.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2020.00811
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Next Articles
LEI Yi1,2,3( ), XIA Qi2,4, MO Zhifeng2,5, LI Hong2,3
), XIA Qi2,4, MO Zhifeng2,5, LI Hong2,3
Received:2018-01-21
Published:2020-07-25
Online:2020-05-25
Contact:
LEI Yi
E-mail:leiyi821@vip.sina.com
Supported by:LEI Yi, XIA Qi, MO Zhifeng, LI Hong. (2020). The attention bias effect of infant face: The mechanism of cuteness and familiarity. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 52(7), 811-822.
| Image matching type | Consistent | Inconsistent | Partial fraction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | |
| High-cute, high-familiar baby face Neutral adult face | 221 | 75 | 235 | 84 | 6.82 | 14.13 |
| High-cute, low-familiar baby face Neutral adult face | 219 | 76 | 229 | 82 | 4.84 | 12.40 |
| Low-cute, high-familiar baby face Neutral adult face | 220 | 78 | 225 | 75 | 2.66 | 11.37 |
| Low-cute, low-familiar baby face Neutral adult face | 226 | 79 | 223 | 79 | -1.05 | 10.53 |
Table 1 Response time to consistent and inconsistent detection points (M ± SD, ms)
| Image matching type | Consistent | Inconsistent | Partial fraction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | |
| High-cute, high-familiar baby face Neutral adult face | 221 | 75 | 235 | 84 | 6.82 | 14.13 |
| High-cute, low-familiar baby face Neutral adult face | 219 | 76 | 229 | 82 | 4.84 | 12.40 |
| Low-cute, high-familiar baby face Neutral adult face | 220 | 78 | 225 | 75 | 2.66 | 11.37 |
| Low-cute, low-familiar baby face Neutral adult face | 226 | 79 | 223 | 79 | -1.05 | 10.53 |

Figure 2. Attention bias score in response time: the attention bias index of different infant faces under high and low familiarity. The histogram error line represents the standard error of the mean under this condition. * p < 0.05.
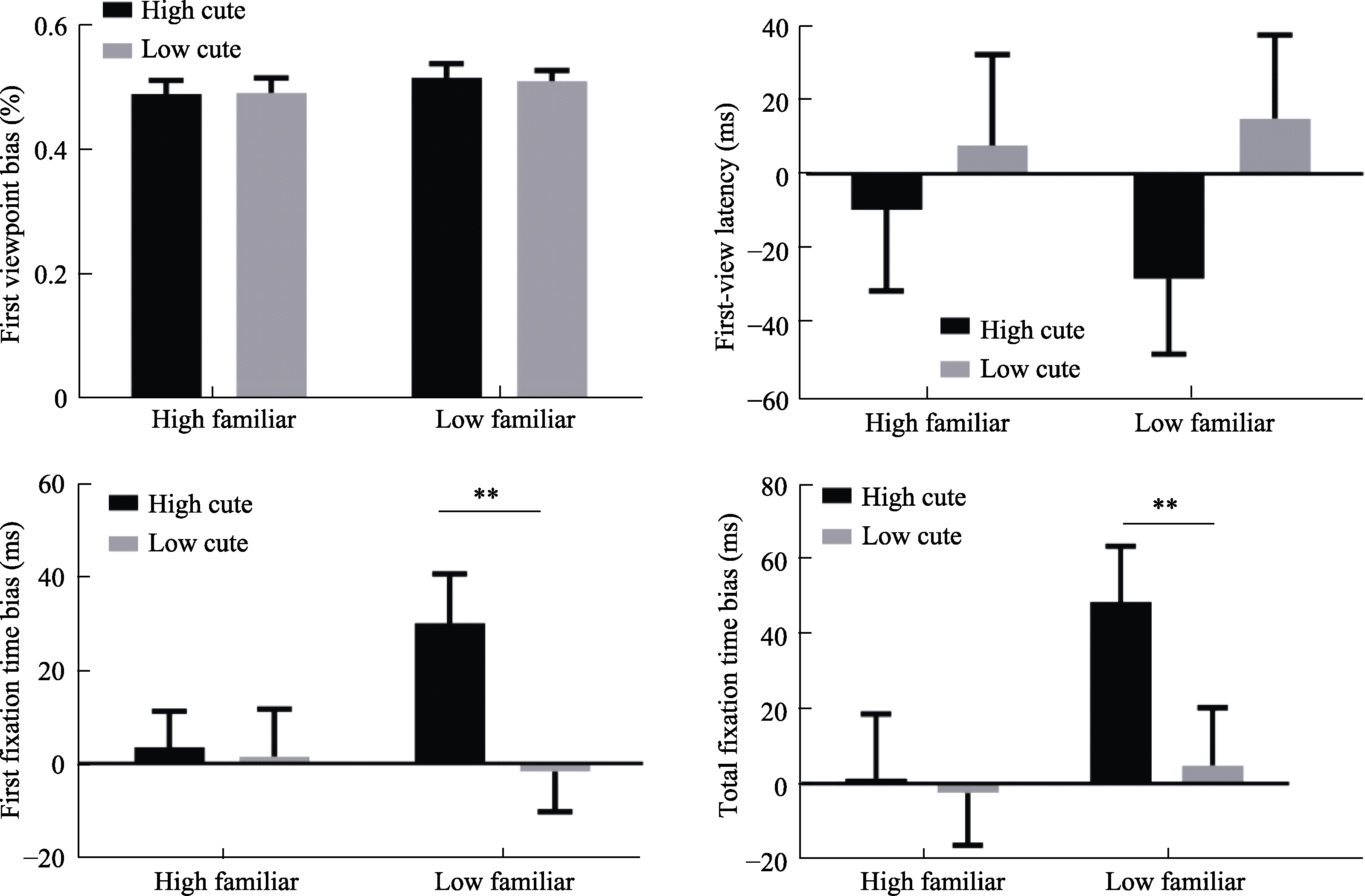
Figure 3. Results: There were 4 kinds of eye movement indexes: Orientation bias, latency bias, gaze time bias and gaze time bias in the region of interest. The histogram error line represents the standard error of the mean under this condition. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.
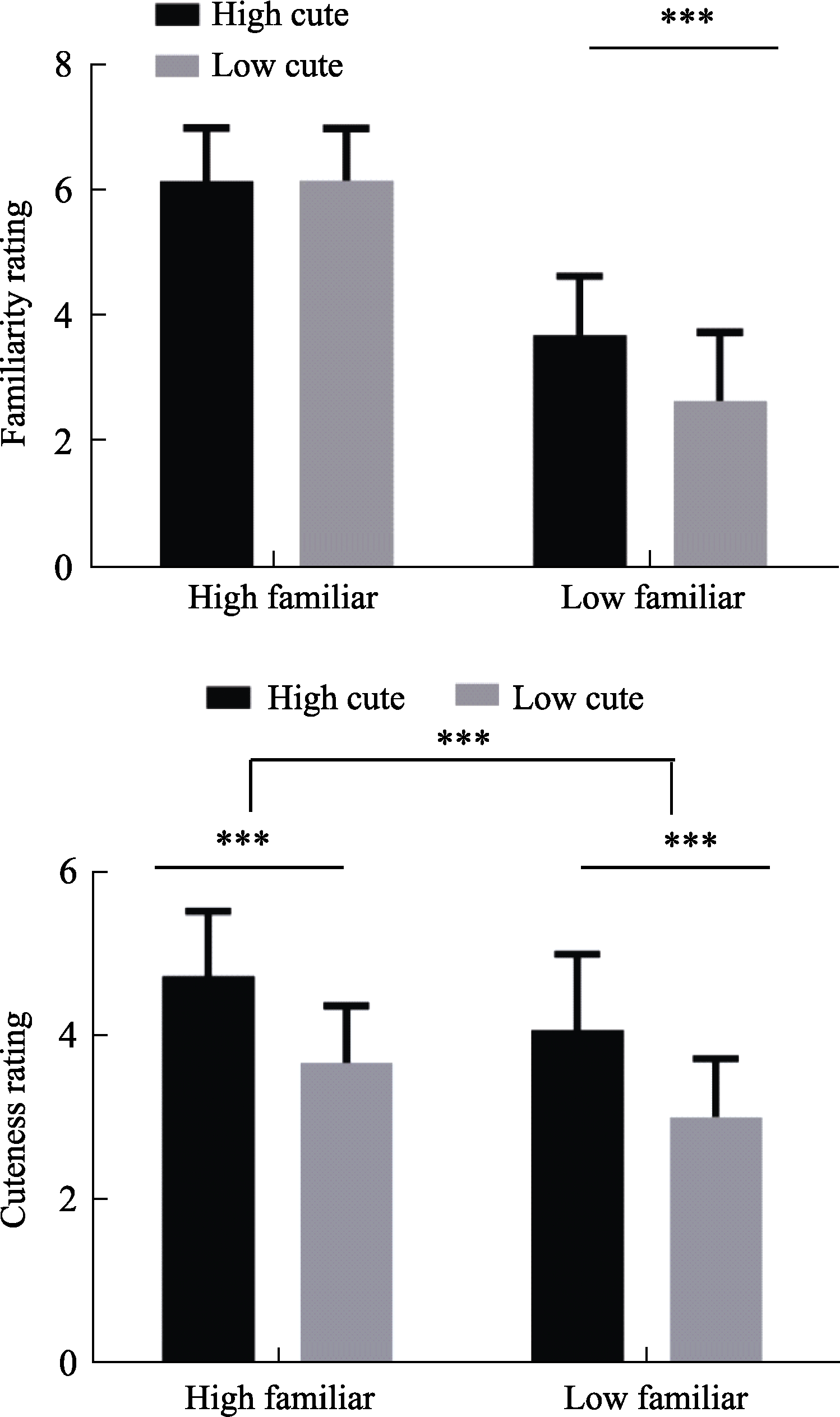
Figure 4. Image Rating: Face Familiarity and Cuteness were rated at the end of the experiment. The histogram error line represents the standard error of the mean under this condition. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
| 1 |
Baeken C., van Schuerbeek P., de Raedt R., Bossuyt A., Vanderhasselt M. A., de Mey J., & Luypaert R . ( 2010). Passively viewing negatively valenced baby faces attenuates left amygdala activity in healthy females scoring high on ‘harm avoidance’. Neuroscience Letters, 478(2, 97-101.
doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.04.073 URL pmid: 20452398 |
| 2 |
Bartels, A.,& Zeki, S.. (2004). The neural correlates of maternal and romantic love. Neuroimage, 21(3, 1155-1166.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.11.003 URL |
| 3 |
Batres C., Kannan M., & Perrett D. I . (2017). Familiarity with own population’s appearance influences facial preferences. Human Nature, 28 (3, 344-354.
doi: 10.1007/s12110-017-9289-8 URL pmid: 28516361 |
| 4 |
Bressan P., Bertamini M., Nalli A., & Zanutto A . ( 2009). Men do not have a stronger preference than women for self-resemblant child faces. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 38 5, 657-664.
doi: 10.1007/s10508-008-9350-0 URL |
| 5 |
Brosch T., Sander D., & Scherer K. R . ( 2007). That baby caught my eye.. attention capture by infant faces. Emotion, 7( 3, 685-689.
doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.7.3.685 URL pmid: 17683225 |
| 6 |
Brosch T., Sander D., Pourtois G., & Scherer K. R . ( 2008). Beyond fear: Rapid spatial orienting toward positive emotional stimuli. Psychological Science, 19 (4, 362-370.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02094.x URL pmid: 18399889 |
| 7 | Cheng G., Zhang D. J., Guan Y. S., & Cheng Y. H . ( 2015). Preliminary establishment of the standardized Chinese infant facial expression of emotion. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 29 6, 406-412. |
| 8 | Damon F., Méary D., Quinn P. C., Lee K., Simpson E. A., Paukner A., … Pascalis O . ( 2017). Preference for facial averageness: Evidence for a common mechanism in human and macaque infants. Scientific Reports, 7, 46303. |
| 9 | Esposito G., Nakazawa J., Ogawa,S., Stival R., Kawashima A., Putnick D. L., & Bornstein M. H . ( 2014). Baby, you light-up my face: Culture-general physiological responses to infants and culture-specific cognitive judgements of adults. Plos One, 9, e106705. |
| 10 | Esposito G., Valenzi S., Islam T., Mash C., & Bornstein M. H . ( 2015). Immediate and selective maternal brain responses to own infant faces. Behavioural Brain Research, 116, 40-43. |
| 11 |
Garcia-Marques T., Mackie D. M., Claypool H. M., & Garcia-Marques L . ( 2004). Positivity can cue familiarity. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 30( 5, 585-593.
doi: 10.1177/0146167203262856 URL pmid: 15107158 |
| 12 | Garcia-Marques T., Prada M., & Mackie D. M . ( 2016). Familiarity increases subjective positive affect even in non-affective and non-evaluative contexts. Motivation & Emotion, 40 4, 638-645. |
| 13 |
Glocker M. L., Langleben D. D., Ruparel K., Loughead J. W., Gur R. C., & Sachser N . ( 2009 a). Baby schema in infant faces induces cuteness perception and motivation for caretaking in adults. Ethology, 115 3, 257-263.
doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0310.2008.01603.x URL pmid: 22267884 |
| 14 |
Glocker M. L., Langleben D. D., Ruparel K., Loughead J. W., Valdez J. N., Griffin M. D., .. Gur R. C . ( 2009 b). Baby schema modulates the brain reward system in nulliparous women. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106 22, 9115-9119.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0811620106 URL pmid: 19451625 |
| 15 |
Gobbini, M. I., & Haxby, J. V . ( 2006). Neural response to the visual familiarity of faces. Brain Research Bulletin, 71 1-3, 76-82.
doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2006.08.003 URL pmid: 17113931 |
| 16 |
Grasso D. J., Moser J. S., Dozier M., & Simons R . ( 2009). ERP correlates of attention allocation in mothers processing faces of their children. Biological Psychology, 81 2, 95-102.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2009.03.001 URL pmid: 19428973 |
| 17 |
Hahn A. C., Debruine L. M., & Jones B. C . ( 2015). Reported maternal tendencies predict the reward value of infant facial cuteness, but not cuteness detection. Biology Letters, 11 3, 20140978.
doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2014.0978 URL pmid: 25740842 |
| 18 |
Hahn A. C., Xiao D., Sprengelmeyer R., & Perrett D. I . ( 2013). Gender differences in the incentive salience of adult and infant faces. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 66 1, 200-208.
doi: 10.1080/17470218.2012.705860 URL |
| 19 |
Henson R., Shallice T., & Dolan R . (2000). Neuroimaging evidence for dissociable forms of repetition priming. Science, 287 5456, 1269-1272.
doi: 10.1126/science.287.5456.1269 URL pmid: 10678834 |
| 20 |
Hildebrandt, K. A., & Fitzgerald, H. E . (1978). Adults’ responses to infants varying in perceived cuteness. Behavioural Processes, 3(2), 159-172.
doi: 10.1016/0376-6357(78)90042-6 URL pmid: 24924654 |
| 21 |
Jasmin C., Tianyi L., Joshua C . ( 2014). The impact of childhood experience on amygdala response to perceptually familiar black and white faces. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 26 9, 1992-2004.
doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_00605 URL |
| 22 |
Koda H., Sato A., & Kato A . ( 2013). Is attentional prioritisation of infant faces unique in humans?: Comparative demonstrations by modified dot-probe task in monkeys. Behavioural Processes, 98 9, 31-36.
doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2013.04.013 URL |
| 23 |
Kou H., Su Y. H., Luo X. C., & Chen H . (2015). Attentional bias toward face-related words among females with facial negative physical self: Evidence from an eye-movement study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 47 10, 1213-1222.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2015.01213 URL |
| 24 |
Kringelbach M. L., Lehtonen A., Squire S., Harvey A. G., Craske M. G., Holliday I. E., .. Stein A . (2008). A specific and rapid neural signature for parental instinct. PLoS One, 3(2), e1664.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001664 URL pmid: 18301742 |
| 25 |
Kringelbach M. L., Stark E. A., Alexander C., Bornstein M. H., & Stein A . ( 2016). On cuteness: Unlocking the parental brain and beyond. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 20(7), 545-558.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2016.05.003 URL pmid: 27211583 |
| 26 | Lee, A. Y . (2001). The mere exposure effect: An uncertainty reduction explanation revisited. Personality & Social Psychology Bulletin, 27 10, 1255-1266. |
| 27 |
Lehmann V., Huis E. M., & Vingerhoets A. J . (2013). The human and animal baby schema effect: Correlates of individual differences. Behavioural processes, 94, 99-108.
doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2013.01.001 URL |
| 28 |
Leibenluft E., Gobbini M. I., Harrison T., & Haxby J. V . (2004). Mothers' neural activation in response to pictures of their children and other children. Biol Psychiatry, 56 4, 225-232.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.05.017 URL pmid: 15312809 |
| 29 |
Lipp, O. V . (2006). Of snakes and flowers: Does preferential detection of pictures of fear-relevant animals in visual search reflect on fear-relevance? Emotion, 6(2, 296-308.
doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.6.2.296 URL pmid: 16768561 |
| 30 |
Lorenz, K.(1943). Die angeborenen Formen möglicher Erfahrung. Zeitschrift FüR Tierpsychologie, 5(2, 235-409.
doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0310.1943.tb00655.x URL |
| 31 |
Lucion M. K., Oliveira V., Bizarro L., Bischoff A. R., Silveira P. P., & Kauer-Sant'Anna M . (2017). Attentional bias toward infant faces-Review of the adaptive and clinical relevance. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 116, 1-8.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2017.02.005 URL pmid: 28192170 |
| 32 |
Luo L., Ma X., Zheng X., Zhao W., Xu L., Becker B., & Kendrick K. M . ( 2015). Neural systems and hormones mediating attraction to infant and child faces. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 970.
doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00970 URL pmid: 26236256 |
| 33 | Luo L. Z., Luo Y., Ju E. X., Ma W. J., & Li H . (2011). Baby schema and sex differences in its process. Advances in Psychological Science, 19 10, 1471-1479. |
| 34 | Mogg K., Bradley B., Miles F., Dixon R . (2004). Time course of attentional bias for threat scenes: Testing the vigilance‐avoidance hypothesis. Cognition & Emotion, 18 5, 689-700. |
| 35 |
Osborne, C. D., & Stevenage, S. V . (2008). Internal feature saliency as a marker of familiarity and configural processing. Visual Cognition, 16( 1, 23-43.
doi: 10.1080/13506280701238073 URL |
| 36 |
Park J., Shimojo E., & Shimojo S . ( 2010). Roles of familiarity and novelty in visual preference judgments are segregated across object categories. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107 33, 14552-14555.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1004374107 URL pmid: 20679235 |
| 37 |
Parsons C. E., Young K. S., Joensson M., Brattico E., Hyam J. A., Stein A., … Kringelbach M. L . ( 2014). Ready for action: A role for the human midbrain in responding to infant vocalizations. Social Cognitive & Affective Neuroscience, 9( 7, 977-984.
doi: 10.1093/scan/nst076 URL pmid: 23720574 |
| 38 |
Peskin, M., & Newell, F. N . ( 2004). Familiarity breeds attraction: Effects of exposure on the attractiveness of typical and distinctive faces. Perception, 33 2, 147-157.
doi: 10.1068/p5028 URL pmid: 15109158 |
| 39 |
Proverbio, A. M., & de Gabriele, V. (2017). The other-race effect does not apply to infant faces: An ERP attentional study. Neuropsychologia, 126, 36-45.
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.03.028 URL pmid: 28365361 |
| 40 | Proverbio A. M., Riva F., Zani A., & Martin E . ( 2011). Is it a baby? Perceived age affects brain processing of faces differently in women and men. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 23 11, 3197-3208. |
| 41 |
Rayson H., Parsons C. E., Young K. S., Goodacre T. E., Kringelbach M. L., & Bonaiuto J. J., … Murray L . ( 2016). Effects of infant cleft lip on adult gaze and perceptions of "cuteness". Cleft Palate Craniofac J, 54 5, 562-570.
doi: 10.1597/16-015 URL pmid: 27223624 |
| 42 |
Sanefuji W., Ohgami H., & Hashiya K . ( 2007). Development of preference for baby faces across species in humans (homo sapiens). Journal of Ethology, 25 3, 249-254.
doi: 10.1007/s10164-006-0018-8 URL |
| 43 |
Schein, S. S., & Langlois, J. H . ( 2015). Unattractive infant faces elicit negative affect from adults. Infant Behavior & Development, 38, 130-134.
doi: 10.1016/j.infbeh.2014.12.009 URL pmid: 25658199 |
| 44 | Schleidt M., Schiefenhővel W., Stanjek K., & Krell R . ( 1980). "Caring for a baby" behavior: Reactions of passersby to a mother and baby. Man-Environment Systems, 10 2, 73-82. |
| 45 |
Senese V. P., de Falco S., Bornstein M. H., Caria A., Buffolino S., & Venuti P . ( 2013). Human infant faces provoke implicit positive affective responses in parents and non-parents alike. PLoS ONE, 8(11, e80379.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080379 URL pmid: 24282537 |
| 46 | Shi, Y. M., & Luo Y. J . ( 2016). Characteristics of attention bias to baby face in college students. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 30 5, 378-383. |
| 47 |
Sprengelmeyer R., Lewis J., Hahn A., & Perrett D. I . ( 2013). Aesthetic and incentive salience of cute infant faces: studies of observer sex, oral contraception and menstrual cycle. PLoS ONE, 8(5, e65844.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065844 URL pmid: 23734262 |
| 48 |
Sui, J., & Liu, C. H . (2009). Can beauty be ignored? Effects of facial attractiveness on covert attention. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 16 2, 276-281.
doi: 10.3758/PBR.16.2.276 URL pmid: 19293094 |
| 49 | Ta N., Cheng G., Zhang D., Jia Y., Ding F., & Xia M . ( 2017). Women’s gender roles affect their visual interest in different infant facial expressions. Personality & Individual Differences, 116, 109-114. |
| 50 |
Thompson-Booth C., Viding E., Mayes L. C., Rutherford H. J. V., Hodsoll S., & Mccrory E. J . (2014). Here's looking at you, kid: Attention to infant emotional faces in mothers and non-mothers. Developmental Science, 17(1, 35-46.
doi: 10.1111/desc.12090 URL pmid: 24341972 |
| 51 | Titchener, E. B . ( 1910). A textbook of psychology. New York, NY: Macmillan. |
| 52 |
Volk, A., & Quinsey, V. L . ( 2002). The influence of infant facial cues on adoption preferences. Human Nature, 13(4, 437-455.
doi: 10.1007/s12110-002-1002-9 URL pmid: 26193089 |
| 53 |
Vuilleumier, P .(2005). How brains beware: Neural mechanisms of emotional attention. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 9(12, 585-594.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2005.10.011 URL pmid: 16289871 |
| 54 | Wang H.-T., Huang S.-S., Huang Y.-S., Sun X.-Y., Zheng X.-F . (2012). The temporal course and habituation tendency of the attention bias to the threaten stimulus in the adolescents with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Psychological Development and Education, 28(3, 255-262. |
| 55 | Wang, Y., & Luo, Y. J . (2005). Standardization and assessment of college students’ facial expression of emotion. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 13(4, 396-398. |
| 56 |
Wittfoth-Schardt D., Gründing J., Wittfoth M., Lanfermann H., Heinrichs M., Domes G., … Waller C . ( 2012). Oxytocin modulates neural reactivity to children’s faces as a function of social salience. Neuropsychopharmacology, 37( 8, 1799-1807.
doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.47 URL |
| 57 |
Yin L., Fan M., Lin L., Sun D., & Wang Z. X . (2017). Attractiveness modulates neural processing of infant faces differently in males and females. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 11, 551.
doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00551 URL pmid: 29184490 |
| 58 |
Young K. S., Parsons C. E., Stein A., & Kringelbach M. L . ( 2015). Motion and emotion: Depression reduces psychomotor performance and alters affective movements in caregiving interactions. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 9, 26.
doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00026 URL pmid: 25741255 |
| 59 |
Zebrowitz L. A., White B., & Wieneke K . (2008). Mere exposure and racial prejudice: Exposure to other-race faces increases liking for strangers of that race. Social Cognition, 26(3, 259-275.
doi: 10.1521/soco.2008.26.3.259 URL pmid: 19584948 |
| 60 |
Zebrowitz, L. A., & Zhang, Y., .(2012). Neural evidence for reduced apprehensiveness of familiarized stimuli in a mere exposure paradigm. Social Neuroscience, 7(4, 347-358.
doi: 10.1080/17470919.2011.628409 URL pmid: 22017290 |
| [1] | FENG Wenting, XU Yuanping, HUANG Hai, WANG Tao. Kawai vs. Whimsical: The influence of cuteness types of luxury brands on consumers' preferences [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(3): 313-330. |
| [2] | ZHANG Ni, LIU Wen, LIU Fang, GUO Xin. Relationship between depression and cognitive reappraisal in 8-12 years old children: the mediating role of attention bias toward sad expression [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(1): 25-39. |
| [3] | ZHOU Wenjie, DENG Liqun, DING Jinhong. Neural mechanism underlying the effects of object color on episodic memory [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(3): 229-243. |
| [4] | REN Zhihong, ZHAO Ziyi, YU Xianglian, ZHAO Chunxiao, ZHANG Lin, LIN Yuzhong, ZHANG Wei. Testosterone and aggressive behavior in juvenile offenders with antisocial tendency: The mediation effect of hostile attention bias and the moderation effect of cortisol [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(11): 1288-1300. |
| [5] | LIU Guixiong,JIA Yongping,WANG Yujuan,MAIHEFULAITI ·Kanji,GUO Chunyan. The bilingual L2 advantage in associative recognition [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2019, 51(1): 14-23. |
| [6] | Jinsheng HU, Chengshi LI, Qi WANG, Songze LI, Taotao LI, Shuqing LIU. The deficiency of attention bias to emotional prosody in the teenagers with autism spectrum disorders: A perceptual mode of low efficiency [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2018, 50(6): 637-646. |
| [7] | LI Tingyu, LIU Li, LI Yilin, ZHU Liqi. Preschoolers' selective trust and belief revision in conflicting situation [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2018, 50(12): 1390-1399. |
| [8] | JIA Yongping; ZHOU Chu; LI Lin; GUO Xiuyan. Recognition without cued recall (RWCR) phenomenon in Chinese characters: Effects of restudying and testing [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2016, 48(2): 111-120. |
| [9] | YE Xiaohong, CHEN Youzhen, MENG Yingfang. Neural Processing of Recollection, Familiarity and Priming at Encoding [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(9): 1101-1110. |
| [10] | MAO Xinrui, XU Huifang, GUO Chunyan. Emotional Memory Enhancement Effect in Dual-processing Recognition Retrieval [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(9): 1111-1123. |
| [11] | WANG Pei;CHEN Li; XIE Yiwen; ZHANG Qin. The Effect of Familiarity and Compatibility on Mental Representation of the Stereotype in Compound Social Categories [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(3): 375-388. |
| [12] | WU Binxing, ZHANG Zhijun, SUN Yusheng. Facial Familiarity Modulates the Interaction between Facial Gender and Emotional Expression [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(10): 1201-1212. |
| [13] | CHEN Yongxiang, ZHU Liqi. Predictors of Action Picture Naming in Mandarin Chinese [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2015, 47(1): 11-18. |
| [14] | WANG Jingxin;JIA Liping;BAI Xuejun;LUO Yuejia. Emotional Faces Processing Takes Precedence of Inhibition of Return: ERPs Study [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2013, 45(1): 1-10. |
| [15] | Zhang-Jijia,Kong Changfeng. Effects of Categorical Variables on Fale Recognition [J]. , 2006, 38(03): 324-332. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||